Ayurveda for autoimmune
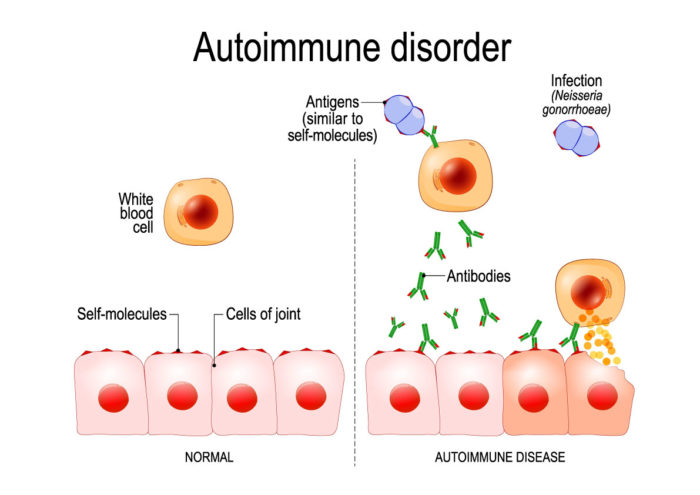
Autoimmunity is the presence of immune responses against self- tissue. It may be harmless phenomenon only by the presence of low-titre auto-antibodies. However, if these responses cause significant organ damage, the autoimmune diseases occurs.
Ayurveda describes this in a slightly different way. Ayurveda suggests that the immune system does not attack the body’s own cells accidentally, but it does so to defend against a form of harmful metabolites of body, called ‘Ama’. Ama is produced in the affected level of tissues. Ama indicates raw, uncooked, unripe, immature, undigested and incompletely oxidized food contents.
Due to the hypo functioning of ushma (metabolic fire), the food which is improperly digested, yields immature Rasa in amasaya and due to retention undergoes fermentation or purification. This state of Rasa is regarded as Ama. It is produced both in cellular and metabolic level.
Causes of autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are usually caused by large amounts of Ama penetrating certain body tissues or physiological systems. In addition, prolonged exposure to poorly digestible food, pollutants, allergens, toxic and synthetic chemicals and drugs is another cause of autoimmune diseases. Poor treatment of the disease and repeated suppression of symptoms without addressing the cause, also accelerates disease progression.
The following factors, alone or in combination with each other, may contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases:
A. The penetration of deep tissues Ama. The reasons for this are as follows:
1. Poor digestion
The digestive system plays the most important metabolic function of the body, and is the basis for all other macro- and micro-metabolic processes that converts and breaking down of all organic substances. Weak digestion leads to the accumulation of incompletely processed metabolites. This, in turn, has an impact on all metabolic processes, allowing the production of Ama, both superficially and on a deeper level rises.
2. Vitiation of Dosha
The Dosha are bio-humors that govern all physiological processes in the body. When the Dosha gets vitiated, cause a variety of diseases. Depletion of doshas leading to metabolic disturbance also causes ama.
3. Accumulation of metabolic waste
Suppressing the natural urges to get rid of metabolic waste, leads to physical obstructions in the discharge channels of the body. The resulting accumulations of waste at different levels of metabolism, does the number of toxins rise, which ultimately leads to an increase in the body Ama.
B. Prolonged exposure to incompatible materials
- Food: Some foods are naturally incompatible and unhealthy for everyone. Other foods are not well tolerated only for people with a certain constitution, while other food is not good for a few people. Normally, many food just to be safe to eat, but in combination with other foods that cannot sometimes be the case. Toxic substances are easy to recognize because they pose a danger acutely. However many people are not aware of the incompatibility of some foods they regularly take to themselves because the only mild symptoms. In short, each individual has different sensitivities and incompatibilities.
- Addictions: The addiction to alcohol, nicotine, drugs, etc. makes the body completely dependent on unhealthy chemicals. In people who are addicted, accumulate toxins that damage the vital organs and the defense mechanism paralyze.
- Medicines: Several drugs used for symptomatic relief, suppress or the superficial symptoms of diseases, but this incomplete treatment of the underlying cause, in fact, the condition complicates. Moreover, excessive use of antibiotics suppresses the natural defenses of the body, and steroids reduce our immunity. All these drugs lead to improper or prolonged use to metabolites that may be incompatible with our body cells.
Clinical features
The clinical presentation of autoimmune disease is highly variable. There are distinguished four type of immune response that result in tissue damage.
- Type I hypersensitivity: Relevant in allergy but not associated with auto- immune disease.
- Type II hypersensitivity: Causes injury to a single tissue or organ and is antibody mediated. Autoimmune hemolytic anaemia, Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura are some examples.
- Type III hypersensitivity: It is immune complex mediated response determined by relative amount of complex, nature of the antigen and local haemodynamics. SLE is the example.
- Type IV hypersensitivity: It is mediated by activated T cells and macrophages which together cause tissue damage as in Type 1 diabetes.
General complains includes
- Fatigue
- achy muscles
- swelling and redness
- low-grade fever
- trouble concentrating
- numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- hair loss
- skin rashes
Diagnosis
No single test can diagnose most autoimmune diseases. Combination of tests and a review of your symptoms and physical examination is used for diagnosis.
The antinuclear antibody test (ANA) is often one of the first tests done when symptoms suggest an autoimmune disease. A positive test means you may have one of these diseases, but it won’t confirm exactly which one you have or if you have one for sure.
Other tests look for specific autoantibodies produced in certain autoimmune diseases.
Management
In spite of use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) and immune- suppressing drugs Ayurveda recommend for use of detox therapy and herbal formulation for the approach of treatment.
| Stage of autoimmune diseases | Treatment approach |
| 1. Mild | o Langhana(Fasting Therapy) |
| 2. Moderate | o Langhana Kriya with pachana drugs( Fasting along with use of pachana drugs) |
| 3. Excessive | o Sodhana kriya ( Detox therapy) |
General treatment approach
- Removal of free radical
- Purification therapy
- Use of anti-oxidant
- Rasayana and Vajikarana therapy